classical electron radius|Quantum Physics I, Lecture Note 3 : Clark • Electromagnetic mass Tingnan ang higit pa MEIA CASSANDRA VIRAL. Join group. Upcoming events
PH0 · Structure and radius of electron
PH1 · Quantum Physics I, Lecture Note 3
PH2 · Electron Radius
PH3 · Classical electron radius
PH4 · Classical Electron Radius
PH5 · Classical
PH6 · CODATA Value: classical electron radius
PH7 · 28 Electromagnetic Mass
The Casino Gaming industry is one of high stakes and high risk, with millions of dollars changing hands daily. As such, it is crucial that casinos have robust compliance and risk management systems in place to protect their assets and maintain the integrity of the industry.
classical electron radius*******The classical electron radius is a combination of fundamental physical quantities that define a length scale for problems involving an electron interacting with electromagnetic radiation. It links the classical electrostatic self-interaction energy of a homogeneous charge distribution to the electron's . Tingnan ang higit paThe classical electron radius length scale can be motivated by considering the energy necessary to assemble an amount of charge $${\displaystyle q}$$ into a sphere of . Tingnan ang higit paThe classical electron radius appears in the classical limit of modern theories as well, including non-relativistic Thomson scattering and the relativistic Tingnan ang higit pa• Length Scales in Physics: the Classical Electron Radius Tingnan ang higit pa• Electromagnetic mass Tingnan ang higit pa
• Arthur N. Cox, Ed. "Allen's Astrophysical Quantities", 4th Ed, Springer, 1999. Tingnan ang higit pa
Learn how the classical electron radius is defined by equating the electrostatic potential energy of a sphere of charge e and radius with the rest energy of the electron. Find the .The classical electron radius is one of a trio of related units of length, the other two being the Bohr radius a0 and the Compton wavelength of the electron λe. The classical .The classical electron radius is a constant that relates the electron charge and mass to the vacuum permittivity. The web page shows its numerical value, standard uncertainty, .The classical electron radius. Before going further some points need to be made about something called the ‘classical electron radius’. This is a calculated radius based on an assumption that the mass-energy .
Learn about the photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, and matter waves in this lecture note from MIT. Find out how Planck's constant h relates to the particle nature of light and .
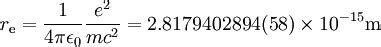
\end{equation} The quantity \begin{equation} \label{Eq:II:28:6} r_0=\frac{e^2}{m_ec^2} \end{equation} is called the “classical electron radius”; it has the numerical value .
classical electron radius Quantum Physics I, Lecture Note 3 \end{equation} The quantity \begin{equation} \label{Eq:II:28:6} r_0=\frac{e^2}{m_ec^2} \end{equation} is called the “classical electron radius”; it has the numerical value .
The classical electron radius is a combination of fundamental physical quantities that define a length scale for problems involving an electron interacting with electromagnetic .
Learn how to calculate the classical electron radius based on a relativistic model of the electron. Find out its numerical value, derivation, and relation to other units of length.Electron Radius. © 1996-2007 Eric W. WeissteinBohr Orbit Combining the energy of the classical electron orbit with the quantization of angular momentum, the Bohr approach yields expressions for the electron orbit radii and energies: Substitution for r gives the Bohr energies and radii: Although the Bohr model of the atom was shown to have many failures, the expression for the hydrogen electron .
Solving for L we get a formula for the electron radius r e. In other words, the classical electron radius is the radius the electron would have to have for all of its mass to be due to the electric field it produced, assuming it was a charged shell. Up to miscellaneous factors we get r e = e 2 /mc 2,古典電子半径(こてんでんしはんけい、英: classical electron radius )とは、ローレンツの電子論(ローレンツのでんしろん、英: Lorentz's theory of electron )の中で論じられる古典的な電子の半径の事で、CODATAから発表される物理定数の1つである。 その値は = = と与えられる(2022 CODATA推奨値 )。To get the classical electron radius re= e^2/4πε0 mc^2, where e,m are the charge and mass of the electron, take one electron at rest in the lab and another at infinity with maximum speed c (or very near to it). The electron looses all its motion/kinetic energy to repulsion as it reaches the static electron- so this radius represents the .So there’s something that’s referred to as the classical electron radius, and it’s equal to the so-called Thomsom scattering length. Thomson scattering, as opposed to Compton scattering, is elastic scattering, so it preserves kinetic energy (unlike Compton scattering, where energy gets absorbed and changes frequencies ).
The classical electron radius is a combination of fundamental physical quantities that define a length scale for problems involving an electron interacting with electromagnetic radiation. It links the classical electrostatic self-interaction energy of a homogeneous charge distribution to the electron's relativistic mass-energy. According to modern .
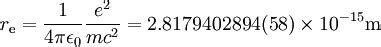
According to one theory, the mass m of the electron arises simply as a consequence of the electrostatic energy of its electric field, through Einstein's famous expression ε=mc^2, where ε is the field energy and c is the speed of light.The energy of the electron's field is found by integrating the field energy density U over all space. If a is the radius of the electron .The electron is an incredibly difficult particle to find, let alone measure. However, the electron classical radius is used throughout physics equations as a value that has been derived, rather than a direct measurement of the particle. The radius is the distance from the electron’s core to the edge of the particle.Quantum Physics I, Lecture Note 3 The classical electron radius. Before going further some points need to be made about something called the ‘classical electron radius’. This is a calculated radius based on an assumption that the mass-energy potential of an electron is fully contained within a certain radius . It has a value .
We define the classical electron radius as \[r_{e}=\frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{e^{2}}{m_{e} c^{2}} \sim 2.8 \mathrm{fm}, \nonumber\] which is the distance at which the Coulomb energy is equal to the rest mass. Although this is not close to the real size of an electron (as for example we would expect the electron radius –if it could be .classical electron radius So there’s something that’s referred to as the classical electron radius, and it’s equal to the so-called Thomsom scattering length. Thomson scattering, as opposed to Compton scattering, is elastic scattering, so it preserves kinetic energy (unlike Compton scattering, where energy gets absorbed and changes frequencies ).
Electron Radius. © 1996-2007 Eric W. WeissteinThe classical electron radius is a combination of fundamental physical quantities that define a length scale for problems involving an electron interacting with electromagnetic radiation. It links the classical electrostatic self-interaction energy of a homogeneous charge distribution to the electron's relativistic mass–energy.Click equation to show only symbol: classical electron radius: Numerical value: 2.817 940 3262 x 10-15 m : Standard uncertainty: 0.000 000 0013 x 10-15 m : Relative standard uncertaintyThe ‘classical electron radius’ is a scientific term used to describe the size of an electron. It’s about 2.8179403227 x 10^-15 meters. The radius of a proton is several times larger than the classical electron radius. The size of an atom is primarily determined by the space where its electrons move around the nucleus.
radius of the electron is the classical electron radius, e2 mc2 ˇ10 13cm (which will be explained in the next section). If you assume that the angular momentum of the electron is due entirely to the spinning of a sphere with this radius and the mass of the electron, points on the edge of the sphere would have to be moving superluminally (Gri .
The classical electron radius is a length scale at which the classical self-energy of the electron completely accounts for the mass. It tells you where the classical theory of a pointlike electron breaks down. The compton wavelength tells you where quantum mechanics takes over. The ratio of the compton wavelength to the classical electron .The radius of the first Bohr orbit is called the Bohr radius of hydrogen, denoted as a 0. a 0. Its value is obtained by setting n = 1 n = 1 in Equation 6.38: . The Bohr model of hydrogen is a semi-classical model because it combines the classical concept of electron orbits with the new concept of quantization. The remarkable success of this .
パブリッシャーのAxolot GamesとデベロッパーのRedbeet Interactiveは6月21日、『Raft』をSteamにて正式リリースした。早期アクセス配信から4年。同作における史上最大のアップデートが実施され物語が完結すると共に、正式リリースを果たした。
classical electron radius|Quantum Physics I, Lecture Note 3